-
JPA 영속성 컨텍스트Java&Spring/Spring 2022. 9. 1. 14:55
영속성 컨텍스트 = 엔티티를 저장 하는 환경
정의: Domain 에서 정의 한다.
엔티티(Entity) = 개체 , 데이터의 집합 , 저장 관리 되는 대상.
--- JPA ----
Spring 에서는 Entity 어노테이션을 붙임으로 정의를 한다 .
1. 모든 Entity 는 pk 를 가지고 있어야한다. @GeneratedValue 를 이용하여 identifier 의 정의 방법을 설정 할 수 있다.
2.
ex)
package hackathon.nomadworker.domain; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnore; import org.locationtech.jts.geom.Point; import javax.persistence.*; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; @Entity @Getter @Setter public class Place { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) @Column(name = "p_id") private long id; private String p_cate; private String p_name; private String p_weekt; private String p_weekndt; private float p_grade; private int p_count; @Column(name = "p_addr") private String p_addr; private String p_image; private String p_storeType; private String rent_price; private float p_latitude; private float p_longitude; private Point p_gpoint; @JsonIgnore @OneToMany(mappedBy = "place", cascade = CascadeType.ALL) private List<Feed> feedList = new ArrayList<>(); @OneToMany(mappedBy = "place", cascade = CascadeType.ALL) private List<User_Place> user_placeList = new ArrayList<>(); public void addFeed(Feed feed) { this.feedList.add(feed); feed.setPlace(this); } }주의 사항 :
The name must not be a reserved literal in the Jakarta Persistence query language.
@Entity 인터페이스의 주석을 참고하면 확인이 가능하다.( 인터페이스라 껍데기만 있다 .)
사용 :
주로 Repository 에서 사용한다
package hackathon.nomadworker.repository; import hackathon.nomadworker.domain.Feed; import hackathon.nomadworker.domain.Place; import hackathon.nomadworker.util.Direction; import hackathon.nomadworker.util.GeometryUtil; import hackathon.nomadworker.util.Location; import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor; import org.locationtech.jts.geom.Point; import org.locationtech.jts.io.ParseException; import org.locationtech.jts.io.WKTReader; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import javax.persistence.Query; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.TypedQuery; import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.util.List; @Repository @RequiredArgsConstructor public class PlaceRepository { @Autowired private final EntityManager em; public Place post(Place place) { em.persist(place); // make point return place; } public Place getPlacesById(Long id) { return em.find(Place.class, id); } public List<Place> findAll() { return em.createQuery("select p from Place p", Place.class) .getResultList(); } public List<Place> findOneByNickName(String placeName) { String jpql = "select p from Place p where p.p_name like :placeName"; TypedQuery<Place> query = em.createQuery(jpql, Place.class).setParameter("placeName", placeName).setMaxResults(1000); return query.getResultList(); } public List<Place> findPlacesByCategory(String place_cat) { String jpql = "select p from Place p where p.p_cate like :place_cat"; TypedQuery<Place> query = em.createQuery(jpql, Place.class).setParameter("place_cat",place_cat).setMaxResults(1000); return query.getResultList(); } public List<Place> getNearByCoordinate(Double latitude, Double longitude, Double distance) { Location northEast = GeometryUtil .calculate(latitude, longitude, distance, Direction.NORTHEAST.getBearing()); Location southWest = GeometryUtil .calculate(latitude, longitude, distance, Direction.SOUTHWEST.getBearing()); double x1 = northEast.getLatitude(); double y1 = northEast.getLongitude(); double x2 = southWest.getLatitude(); double y2 = southWest.getLongitude(); String pointFormat = String.format("'LINESTRING(%f %f, %f %f)')", x1, y1, x2, y2); Query query = em.createNativeQuery("SELECT * \n"+ "From place As p \n" + "WHERE MBRContains(ST_LINESTRINGFROMTEXT(" + pointFormat + ",p.p_gpoint)",Place.class).setMaxResults(15); List<Place> places = query.getResultList(); return places; } public List<Feed> getRecommendPlace() { List<Feed> feed = em.createQuery("select f from Feed f " + "join fetch f.place p " + "order by f.f_like desc ", Feed.class).setMaxResults(10).getResultList(); return feed; } /* public List<Place> searchPlace(String p_cate, String p_storeType, String p_name) { List<Place> place = em.createQuery("select p from Place p " + "where p.p_cate =: p_cate " + "and p.p_storeType =: p_storeType " + "and p.p_name =: p_name ", Place.class) .setParameter("p_cate", p_cate) .setParameter("p_storeType", p_storeType) .setParameter("p_name", p_name) .getResultList(); return place; } */ public List<Place> searchPlace(String p_cate, String p_storeType, String p_name) { String jpql = "select p from Place p where p.p_cate =: p_cate and p.p_storeType =: p_storeType and p.p_name like :p_name"; TypedQuery<Place> query = em.createQuery(jpql, Place.class) .setParameter("p_cate", p_cate) .setParameter("p_storeType", p_storeType) .setParameter("p_name", "%" + p_name + "%").setMaxResults(1000); return query.getResultList(); } public List<Place> searchOneByName(String p_name) { String jpql = "select p from Place p where p.p_name like :p_name"; TypedQuery<Place> query = em.createQuery(jpql, Place.class).setParameter("p_name", "%" + p_name + "%").setMaxResults(1000); return query.getResultList(); } public Place gradePlace(Long p_id){ return em.find(Place.class, p_id); } public void setgradePlace(Long p_id, float p_grade, Integer p_count) { Place place = em.find(Place.class, p_id); p_grade = (float)(Math.round(p_grade * 10) / 10.0); place.setP_grade(p_grade); place.setP_count(p_count); em.merge(place); } }Entity Life cycle
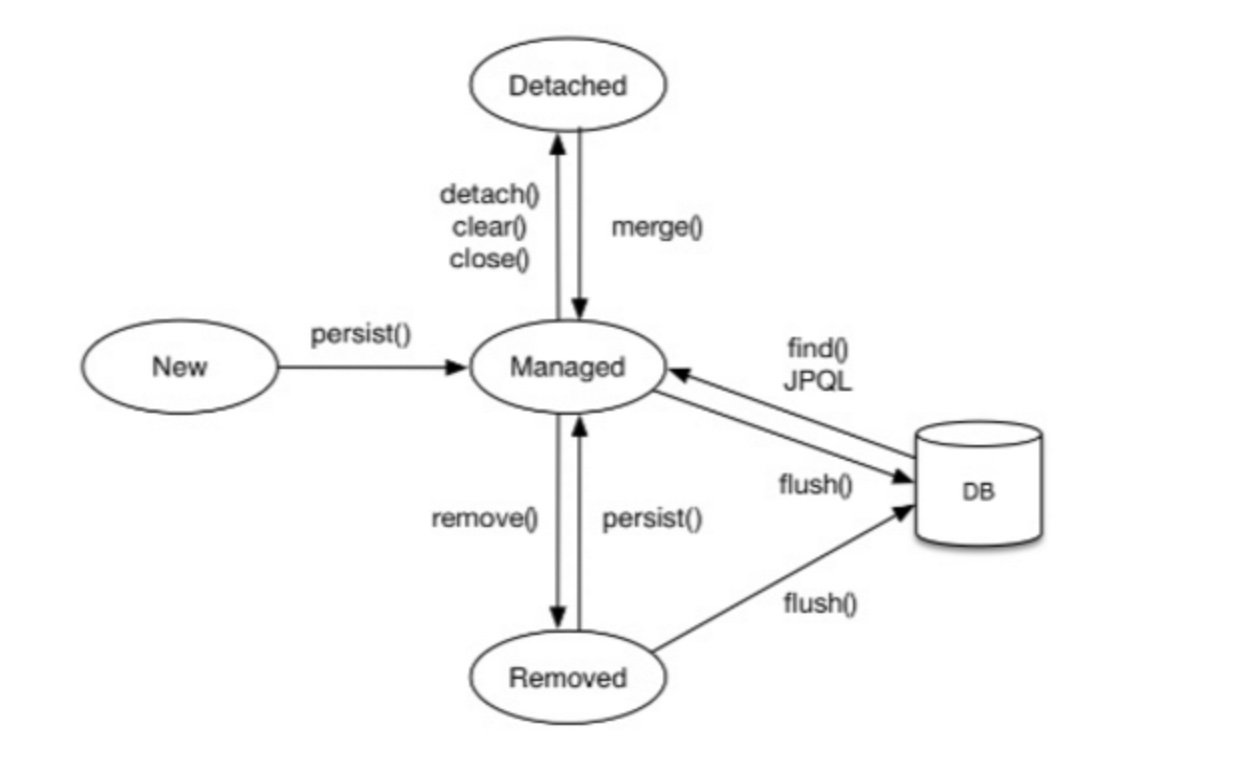
- 비영속(new/transient): 영속성 컨텍스트와 전혀 관계가 없는 상태
- 영속(managed): 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장된 상태
- 준영속(detached): 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장되었다가 분리된 상태
준영속 상태의 특징
1차 캐시 쓰기지연, 변경감지 , 지연 로딩을 포함한 영속성 컨텍스트가 제공히는 어떠한 기능도 동작 x ,
식별자의 값을 가지고 있다.
비영속 : 엔티티 객체를 생성했지만 아직 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장하지않은 상태
ex ) Place place = new Place();
영속 : 엔티티 매니저를 통해 엔티티를 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장한 상태 ,
ex) em.persist(place);
준영속 :영속성 컨텍스트가 관리하던 영속 상태의 엔티티 더이상 관리 하지 않으면 준영속 상태라 부른다.
ex)
// 엔티티를 영속성 컨텍스트에서 분리한후 준영속 상태로 만든다. em.detach(place); // 영속성 콘텍스트를 비워도 관리되던 엔티티는 준영속 상태가 된다. em.claer(); // 영속성 콘텍스트를 종료해도 관리되던 엔티티는 준영속 상태가 된다. em.close();삭제 : 엔티티를 영속성 컨텍스트와 데이터베이스에서 삭제 한다.
em.remove(place);영속성 컨텍스트의 특징 .
영속성 컨텍스트의 식별자 값,
영속성 컨텍스트는 엔티티를 식별자 값으로 구분한다.
영속성 컨텍스트를 DB에 저장 .
JPA는 보통 트랜잭션을 커밋하는 순간 영속성 컨텍스트에 새로 저장된 엔티티를 DB 에 반영 하는데 이를 flush 라고 한다.
참고 :
'Java&Spring > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
@Qualifier (0) 2022.10.31 Spring data Jpa camelCase 자동 underscore 방지 Mysql (0) 2022.09.19 Spring Test 기초[1] , assertall() (0) 2022.09.06 Spring & JPA persist 자동 생성 id 받기 (0) 2022.08.26 스프링 커맨드로 빌드 (0) 2022.06.30